In today’s data-driven world, effective data stewardship and governance are fundamental to leveraging data as a strategic asset. As organizations increasingly rely on data to guide decision-making, these interconnected disciplines provide the foundation for managing data as a valued corporate resource.
At its core, data stewardship involves the custodianship of data. Stewards are tasked with overseeing data quality, accessibility, and integrity throughout its lifecycle. They serve as human custodians of data, drawing on domain expertise to ensure data alignment with organizational goals. Stewardship demands both a nuanced understanding of the data itself and its implications across the business.

Data governance establishes the strategic policies and frameworks for data management. It focuses on compliance, security and scalable processes to dictate how data is governed across the organization. Governance provides the blueprint for stewardship activities, ensuring data is handled ethically, legally and efficiently.
Working in tandem, governance and stewardship transform data from passive information into an active asset. They empower organizations to tap analytics, AI and other technologies to derive value from data. As data volumes grow more complex, these competencies become imperative.
Evolving Traditional Data Governance in the Age of Artificial Intelligence

Let us explore the evolution of stewardship and governance in the age of AI. We examine how stewardship expands from focusing solely on past data to governing continuous real-time data streams. Meanwhile, governance must address emerging risks like bias in AI as well as new data types generated by emerging technologies. Developing agile yet consistent data policies and human oversight is essential in the rapid pace of innovation.
Effective data stewardship and governance remain central to competing in the digital economy. Those able to navigate their expanding complexity will be best positioned to leverage data for a competitive advantage.
The Fundamental Role of Data Stewardship in the Governance Model
Data stewardship is an integral part of the broader data governance operating model, seamlessly interacting with various levels and components of the program. Understanding this interplay is crucial for organizations to ensure the coherence and effectiveness of their data governance initiatives.
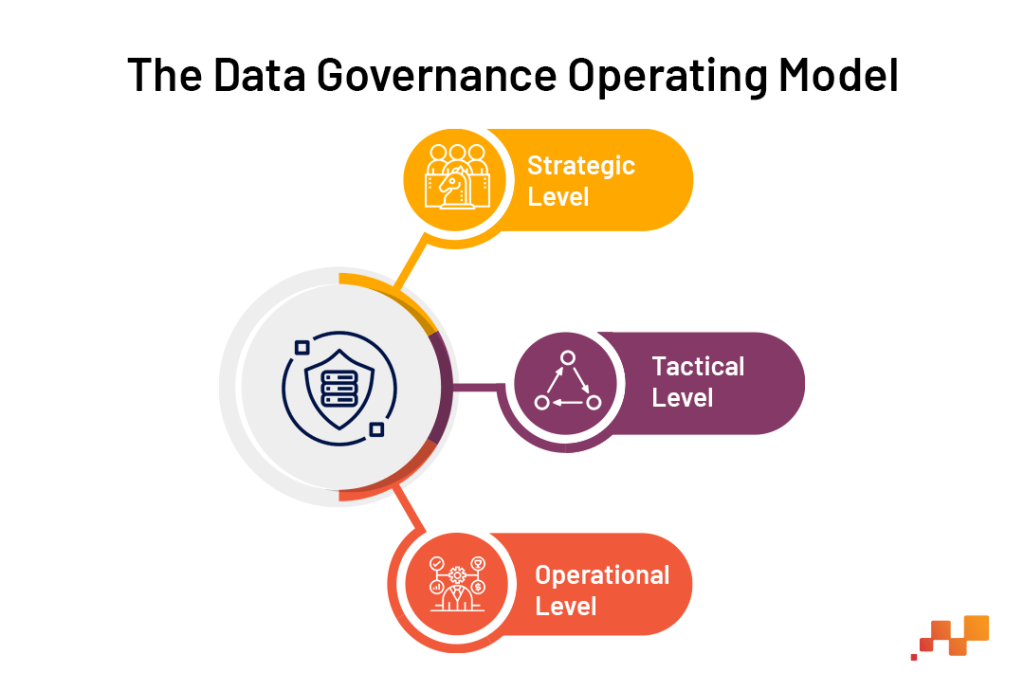
A typical data governance operating model comprises multiple layers, each with distinct but interrelated roles and responsibilities:
Strategic Level: This top layer involves senior management and decision-makers who set the overall direction and policies for data governance. They define the goals, objectives, and key performance indicators (KPIs) that drive the data governance strategy.
Tactical Level: This middle layer includes data governance managers and coordinators who translate the strategic vision into actionable plans. They are responsible for managing the day-to-day aspects of the data governance program, aligning initiatives with business goals.
Operational Level: At this ground level, data stewards and other data professionals implement the policies and procedures. They are the hands-on workforce managing, maintaining, and optimizing data assets.
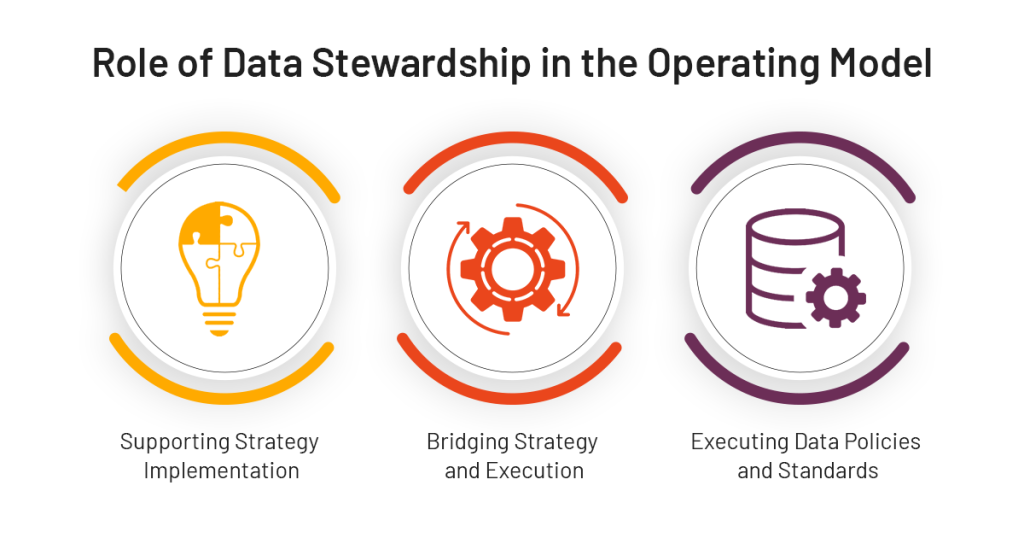
Data stewardship intersects with each layer of the data governance model, playing a vital role in its success:
Supporting Strategy Implementation: Data stewards provide valuable insights and feedback to the strategic level, helping refine goals and policies based on their hands-on experience with data.
Bridging Strategy and Execution: At the tactical level, stewards collaborate with data governance managers to develop practical approaches for policy implementation, data quality improvement, and compliance management.
Executing Data Policies and Standards: On the operational front, stewards are key players in enforcing data governance policies, managing data quality, ensuring compliance, and educating other data users.
Understanding this intricate relationship between data stewardship and the data governance operating model is pivotal for organizations. It ensures that data governance efforts are not only strategically sound but also practically effective, fostering a culture of responsible and efficient data management.
Data stewardship, as a critical component of data governance, is built on several foundational pillars. These elements form the bedrock upon which successful data management strategies are constructed.
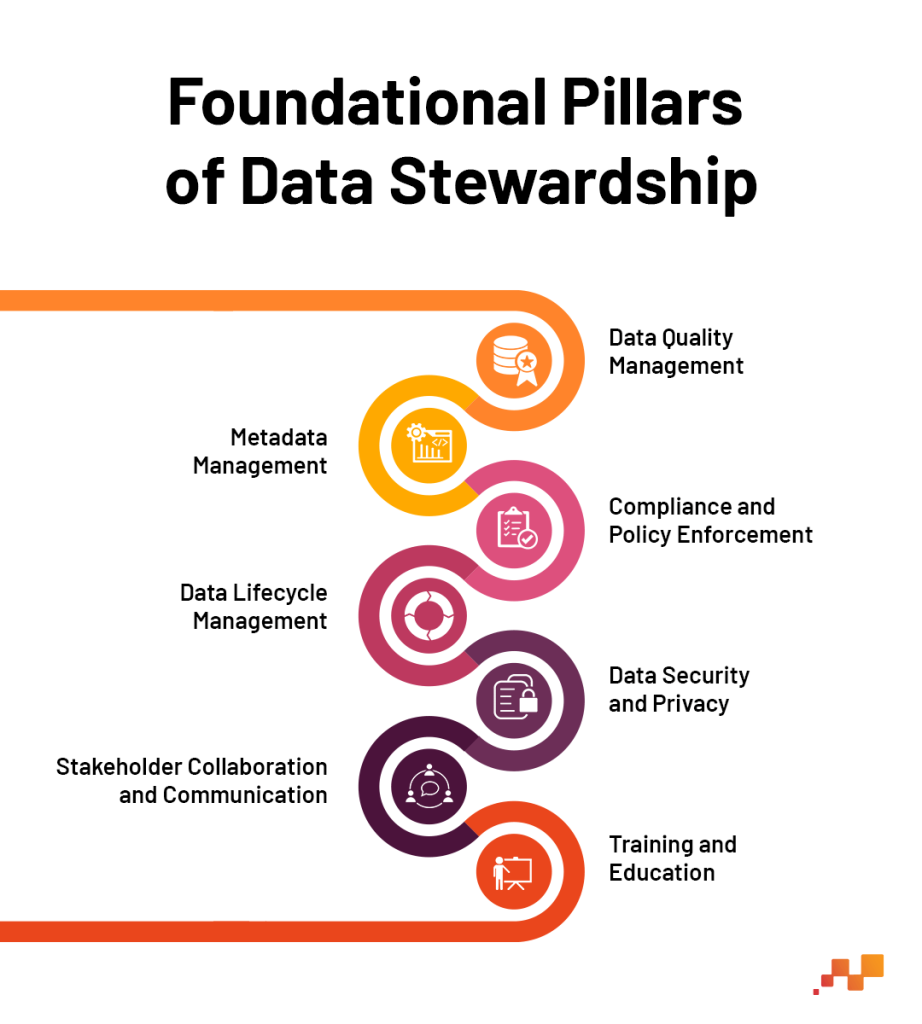
Data Quality Management: At the heart of data stewardship lies the commitment to maintaining high data quality. This involves ensuring accuracy, consistency, and reliability of data across all systems. Data stewards play a pivotal role in setting data quality standards, performing regular audits, and initiating corrective measures to rectify any issues.
Metadata Management: Effective data stewardship requires a thorough understanding and documentation of metadata. Stewards ensure that metadata accurately represents the data, including its source, structure, and usage guidelines. This facilitates better data understanding and governance across the organization.
Compliance and Policy Enforcement: Data stewards ensure adherence to internal policies and external regulatory requirements. They are instrumental in interpreting these regulations in the context of the organization’s data and implementing appropriate controls and processes.
Data Lifecycle Management: Stewards oversee the entire lifecycle of data, from creation and storage to archiving and deletion. They ensure that data is managed efficiently throughout its lifecycle, aligning with the organization’s data strategy and compliance requirements.
Data Security and Privacy: With increasing concerns around data breaches and privacy violations, data stewards are tasked with safeguarding sensitive information. They work closely with IT and security teams to implement robust access controls, encryption, and other security measures.
Stakeholder Collaboration and Communication: Effective data stewardship involves collaboration with various stakeholders, including IT, business units, and external partners. Stewards act as a bridge between these groups, ensuring clear communication and understanding of data-related matters.
Training and Education: Data stewards often lead initiatives to educate and train staff on best practices in Data Governance, policies, and tools. This empowers employees to make informed decisions and fosters a culture of data literacy within the organization.
These foundational elements set the stage for effective data stewardship. As we look towards the future, these principles remain relevant but must adapt to accommodate emerging technologies like AI, reshaping the role of data stewards in the process.
Reframing Data Stewardship in the AI Era
Paradigm Shift in Data Management with AI Integration
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into data management signifies a paradigm shift, redefining traditional data governance frameworks. This transformation is most evident in the role of data stewards, who now face new challenges and opportunities in an AI-enhanced landscape.
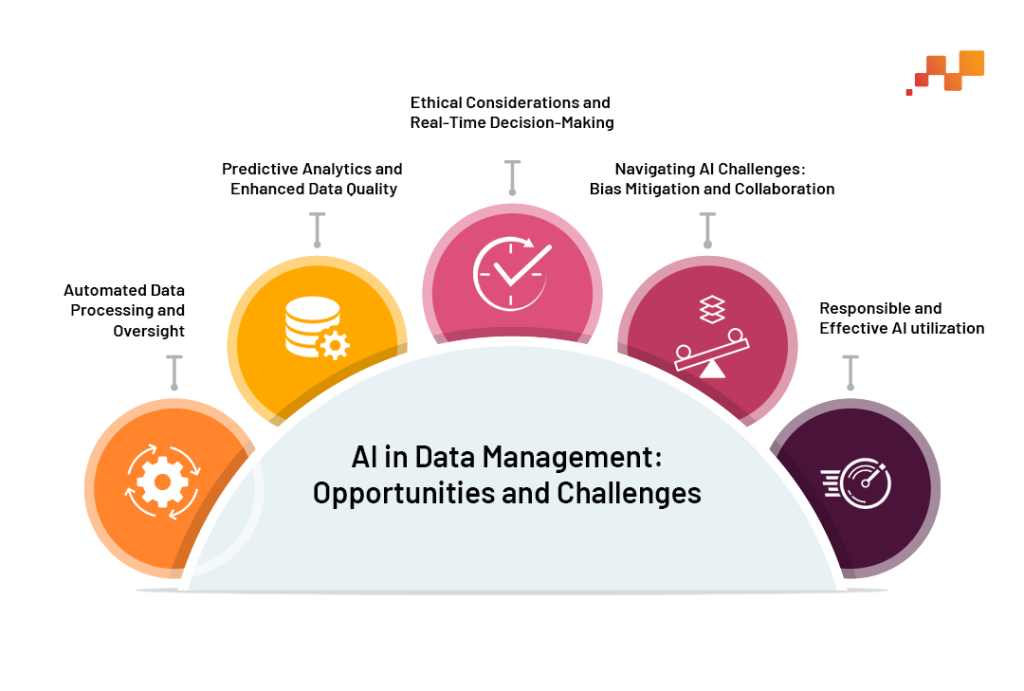
Automated Data Processing and Oversight: AI’s capability to automate complex data tasks, such as cleaning and classification, alters the data steward’s role. Stewards now focus on overseeing these automated processes, ensuring they align with governance standards and maintain data integrity.
Predictive Analytics and Enhanced Data Quality: AI’s predictive analytics tools enable organizations to forecast future trends, necessitating a deeper understanding from data stewards of how these models align with governance policies. Additionally, AI-driven data quality management demands a vigilant approach from stewards to validate and oversee the quality of AI outputs.
Ethical Considerations and Real-Time Decision-Making: As AI processes vast data volumes, ethical considerations and data privacy become paramount. Data stewards must ensure that AI systems adhere to ethical guidelines and data privacy laws. Their role extends to supporting real-time decision-making, backed by reliable, compliant data.
Navigating AI Challenges, Bias Mitigation and Collaboration: The complexity of AI in data governance introduces unique challenges, such as bias in AI models and the need for comprehensive training data oversight. Data stewards must collaborate closely with data scientists and IT teams to ensure ethical AI use and alignment with regulatory compliance.
The Transformative Role in the AI Era: Data stewards in the AI era are pivotal in ensuring safe, responsible, and effective AI utilization. They are now integral to navigating the complexities of AI-driven decision-making, ensuring data integrity, and fostering ethical AI practices. This evolution reflects the heightened significance of data stewardship, making them enablers of innovation and guardians of data governance in an AI-dominated landscape.
Framework for AI-Enhanced Data Stewardship
As organizations navigate the intersection of AI and data management, developing a framework for AI-enhanced data stewardship is crucial. This framework should not only accommodate the integration of AI into stewardship practices but also address the broader implications of ethics, transparency, and continuous learning.
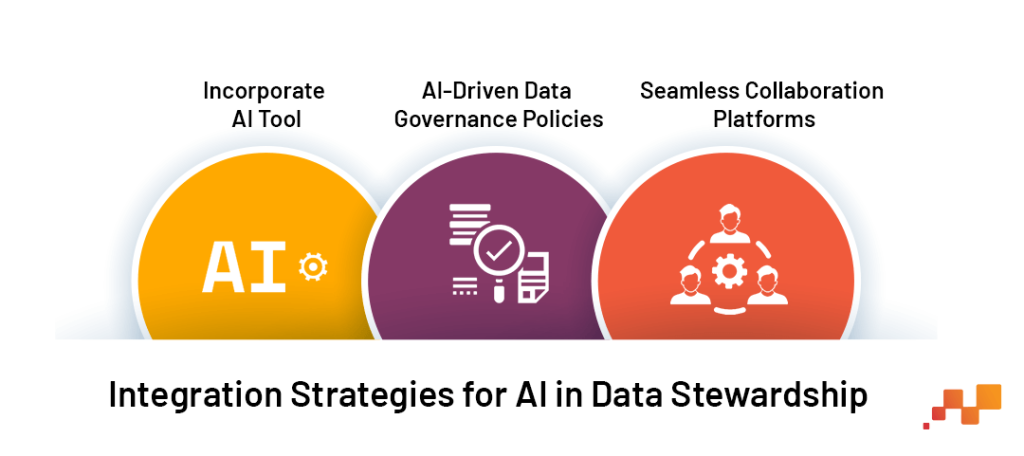
Incorporate AI Tools: Leverage AI tools for data quality management, pattern recognition, and predictive analytics, integrating these into the data stewardship toolkit.
AI-Driven Data Governance Policies: Update data governance policies to include AI-specific considerations, such as the ethical use of AI, data privacy concerns, and AI bias mitigation strategies.
Seamless Collaboration Platforms: Foster environments where data stewards can seamlessly collaborate with data scientists and IT professionals, enhancing cross-disciplinary understanding and governance effectiveness.

Ethics and Transparency: Ethical considerations should be at the forefront, ensuring that AI systems are transparent, fair, and devoid of biases. This requires a methodology that continually assesses AI decisions and their impact on data privacy and security.
Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Embrace a culture of ongoing learning and flexibility, allowing data stewards to stay abreast of AI advancements and their implications for data governance.
Pioneering Tools and Practices: Acknowledge and utilize pioneering tools in the field that facilitate AI integration in data stewardship. Tools like TensorFlow for AI model building, and platforms like Informatica and Talend for data integration, can be instrumental in bridging the gap between traditional data stewardship and AI-driven data management.
This framework outlines a pathway for integrating AI into data stewardship, emphasizing the need for updated governance policies, ethical considerations, and continuous learning. It underscores the importance of leveraging pioneering tools and adopting methodologies that align with the evolving nature of data stewardship in an AI-enhanced world.
Future Direction of Data Management and Governance
As we delve into the transformative landscape of AI in data management, the imperative of foundational data stewardship becomes increasingly clear. The role of data stewards is not merely evolving; it is becoming pivotal in navigating new challenges and opportunities presented by AI. In this context, taking the initial steps to establish a robust data stewardship program, grounded in traditional roles, is more than a strategic move—it is an essential preparation for the inevitable changes brought by AI.
Organizations at the nascent stages of data governance should prioritize setting up a well-structured data stewardship program. This foundational step is crucial in managing the complexities of today’s data landscape and in creating a solid platform for future advancements. By focusing on traditional Data Stewardship Roles—overseeing data quality, accessibility, and alignment with business goals—organizations can build a resilient framework capable of adapting to AI-driven transformations.

For those already equipped with a data stewardship program, now is the time to reinforce and refine these efforts. Strengthening your program means not only ensuring it performs effectively in its current scope but also preparing it for the expanded responsibilities that AI integration will entail. As data stewardship becomes an integral part of your organization’s data governance framework, its formalization and integration with other data management functions will be key to navigating the AI era successfully.
In summary, as AI continues to redefine the data governance landscape, the need for robust, adaptable data stewardship becomes more crucial than ever. Whether you are building your stewardship program from the ground up or fortifying an existing one, doing so with an eye towards the future will position your organization to leverage AI safely, responsibly, and effectively. Embracing AI-enhanced stewardship is not just about integrating cutting-edge tools and adopting new frameworks; it’s about laying the groundwork today for the dynamic role of data stewards in guiding ethical AI deployment and ensuring data integrity in the increasingly automated world of tomorrow.

FAQ’s
Data governance is sometimes described as having different levels. Can you explain the responsibilities at each level?
Absolutely! Data governance typically has three levels. The top level, often led by senior management, sets the overall goals and direction for how data should be managed within the organization. The middle level translates these goals into actionable plans, outlining specific procedures and policies. Finally, the bottom level, which often includes data stewards and specialists, implements these plans and ensures the smooth day-to-day management of the data.
Data stewards seem to have a wider role than just ensuring data quality. What other areas do they manage?
Data stewards act as guardians of the organization’s data. While ensuring data quality is a crucial aspect, their role goes beyond that. They also manage data access, controlling who can view and modify data sets. Additionally, they play a vital role in ensuring compliance with internal data policies and external regulations. Finally, data stewards educate staff on data best practices, fostering a data-literate organization.
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence (AI), how will the responsibilities of data stewards transform?
The rise of AI brings new challenges and responsibilities for data stewards. Traditionally, they focused on human-generated data. Now, they need to oversee how AI processes data, ensuring it aligns with existing data governance standards. This might involve working with data scientists to understand AI models and their data consumption. Collaboration becomes key as data stewards become crucial partners in ensuring ethical AI practices.
The concept of AI-powered data quality management sounds interesting. Can you give a specific example of how this might work?
Imagine a company uses AI to analyze customer reviews in real-time. Traditionally, data stewards might manually review samples of reviews. However, with AI, they can leverage AI tools to automatically identify unusual patterns in sentiment or language. These tools could flag potential issues, like a sudden surge in negative reviews, allowing data stewards to investigate and ensure the data reflects reality.
Smaller businesses are starting to leverage AI. How can they approach data governance in this new environment?
;Even smaller businesses can benefit from data governance in the age of AI. A good first step is to appoint a data champion, someone who understands data best practices and can oversee data quality and compliance. Additionally, there are now affordable cloud-based data governance tools available, making it easier for smaller businesses to manage data access and user permissions. Finally, by focusing on core data quality for the data most critical to their AI initiatives, smaller businesses can navigate the complexities of data governance and ensure the success of their AI projects.